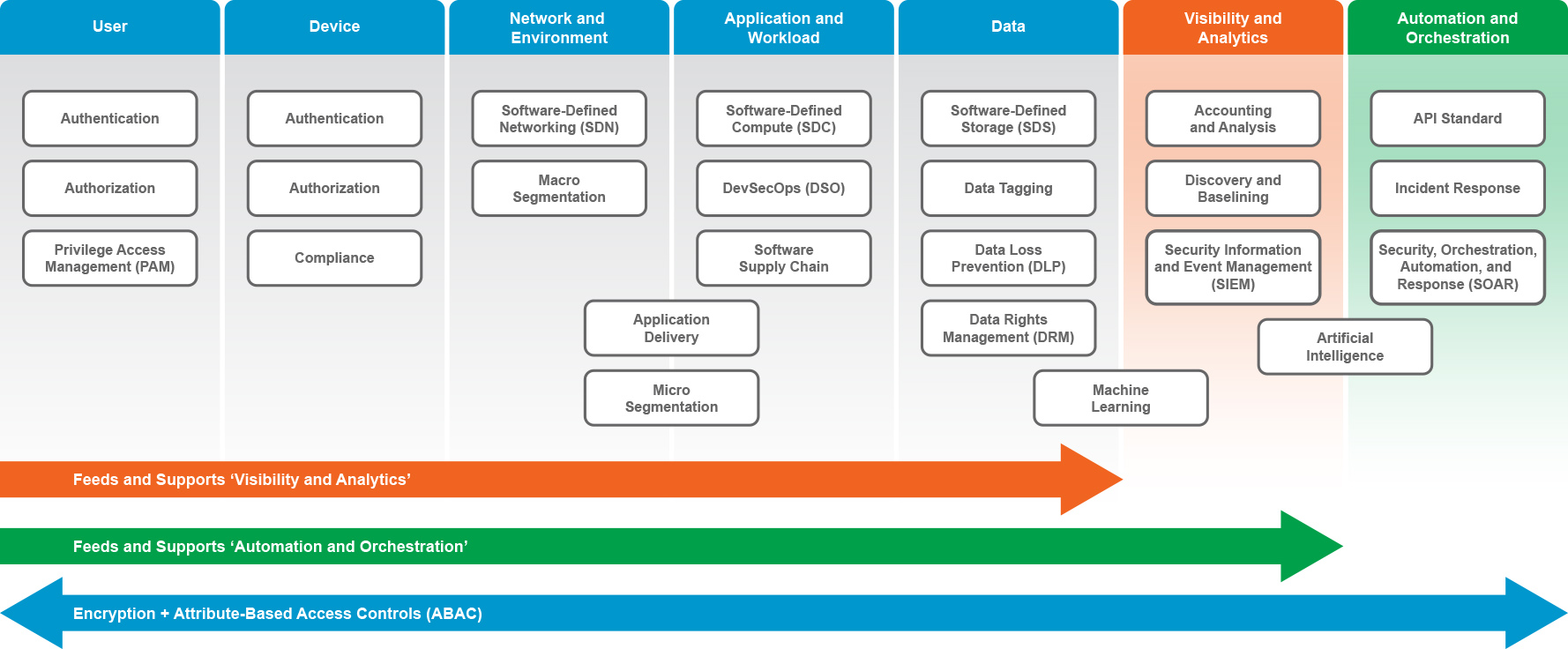
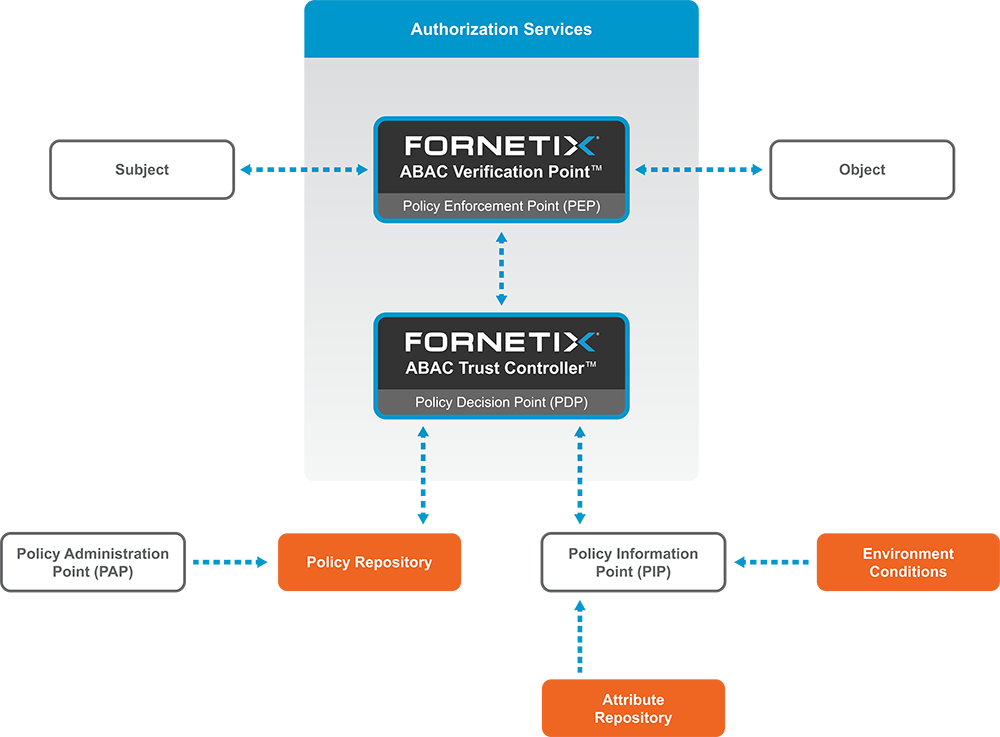
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) is a modern security model that uses a wide variety of defined attributes to determine which users can access your data. Traditional access controls have focused primarily on a role-based model (RBAC) for securing sensitive assets. Organizations needed to predefine all potential functions and assign each user a certain level of security privileges, granting or denying access to data based entirely on their role. This rigid, one-size-fits-all method quickly becomes unwieldy and error-prone with significant security risks when deployed at scale.
As an attribute-based model, ABAC allows for the use of fine-grained, centralized policies to govern whether a user can access the desired data. Instead of rigid roles, ABAC leverages a wide variety of attributes as building blocks to construct meaningful policies. For example, a policy might dictate specific locations, approved devices, certain hours of the day, whitelisted IP addresses, security classifications, department membership, and many other contextual details. Access to the resource is denied if the circumstances fail any of the policy’s requirements.
In a time of increasing collaboration and sharing between enterprises and partners, dynamic and flexible access controls are a non-negotiable requirement for protecting critical assets.